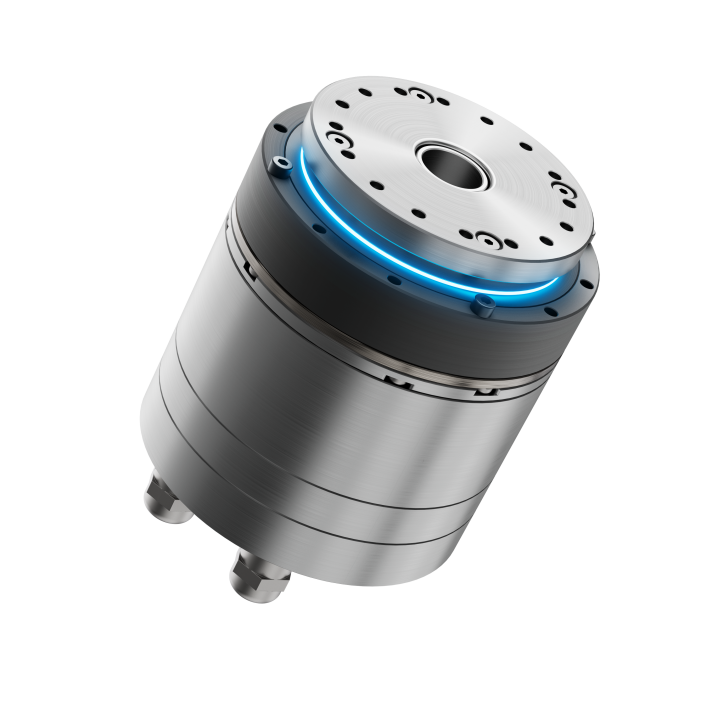
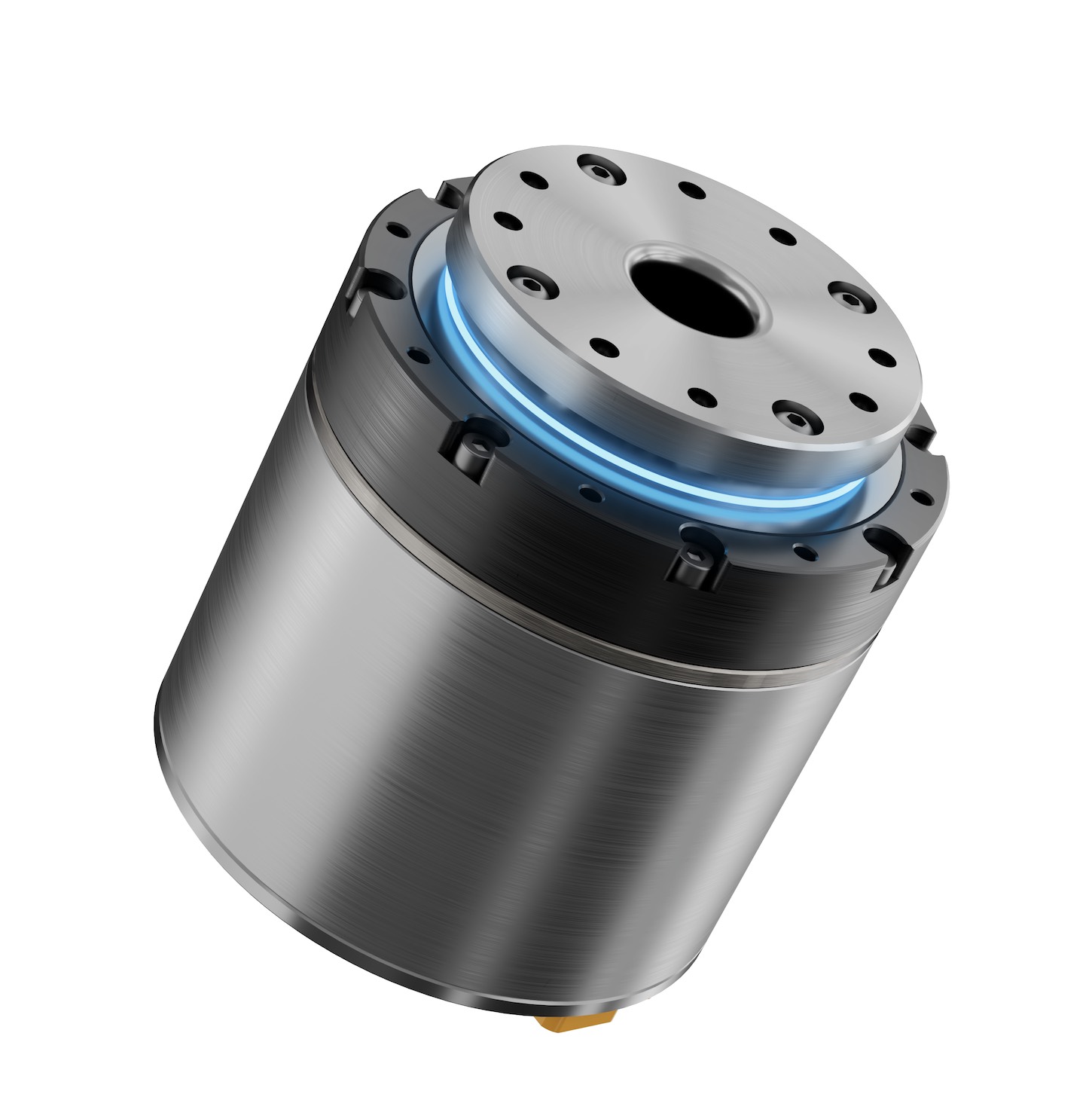
LSS High Precision Harmonic Gearbox
LSS series adopts our newest developed 'LS' tooth profile, equipped to support external loads, featuring high rigidity cross roller bearings, making it a combination product that is easy to operate.
Key Features
- Cup-shaped structure
- Compact and concise design
- Zero backlash
- Input and output coaxial
- Excellent positional accuracy and repeatability.
- Product Description
- Specifications
- Product Video
- Application
- FAQ
- Download
Product Description
The LSS series of micro harmonic reducers can be divided into two models depending on the different used harmonic waveform generators: LSS-I (uni-body type wave generator) and LSS-II (cross slider type wave generator).
We provide 8 different sizes with 5 kinds of speed reduction ratios according to clients' various applications and requirements. The LSS series of harmonic reducer is a combination series that is easy to operate. Standard servo motors can be attached in a compact manner. Each model contains a cross roller bearing with high rigidity to support external loads.
Advantages
Cup-shaped structure, high torque capacity, high stiffness, standard barrel structure with high rigidity full roller cross bearings and long lifespan.
LS tooth profile design, self-developed CMP heat treatment process, 1um track precision grinding, providing higher rigidity, precision, and torque.
Compact and concise design with zero backlash, direct motor connection for convenient installation.
Input and output coaxial.
Excellent positional accuracy and repeatability..
Specifications
Specification of LSS/LSN Rated parameters
| Model | Reduction ratio | Rated torque at 2000r/min input | Permissible peak torque at start and stop | Permissible maximum value for average load torque | Permissible maximum momentary torque | Permissible maximum input rotational speed | Permissible average input rotational speed | Backlash | Weight | Design life | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grease | Grease | |||||||||||||
| Nm | kgfm | Nm | kgfm | Nm | kgfm | Nm | kgfm | r/min | r/min | Arc Sec | kg | Hour | ||
| 8 | 50 | 1.8 | 0.18 | 3.3 | 0.34 | 2.3 | 0.23 | 6.6 | 0.67 | 8500 | 3500 | ≤40 | LSN-I:0.08 | 10000 |
| 100 | 2.4 | 0.24 | 4.8 | 0.49 | 3.3 | 0.34 | 9.0 | 0.92 | 10000 | |||||
| 11 | 50 | 3.5 | 0.36 | 8.3 | 0.85 | 5.5 | 0.56 | 17 | 1.73 | 8500 | 3500 | ≤30 |
LSS-I:0.25 LSN-I:0.17 |
10000 |
| 80 | 4.5 | 0.46 | 9.9 | 1.01 | 8.0 | 0.82 | 22.5 | 2.30 | 10000 | |||||
| 100 | 5 | 0.51 | 11 | 1.12 | 8.9 | 0.91 | 25.0 | 2.55 | 10000 | |||||
| 14 | 50 | 5.4 | 0.55 | 18 | 1.8 | 6.9 | 0.7 | 35 | 3.6 | 8500 | 3500 | ≤20 |
LSS-I/II:0.51 LSS-C:0.09 LSN-I/II:0.39 LSSF-I:0.51 |
10000 |
| 80 | 7.8 | 0.8 | 23 | 2.4 | 11 | 1.1 | 47 | 4.8 | 15000 | |||||
| 100 | 7.8 | 0.8 | 28 | 2.9 | 11 | 1.1 | 54 | 5.5 | 15000 | |||||
| 120 | 7.8 | 0.8 | 28 | 2.9 | 11 | 1.1 | 54 | 5.5 | 15000 | |||||
| 17 | 50 | 16 | 1.6 | 34 | 3.5 | 26 | 2.6 | 70 | 7.1 | 7300 | 3500 | ≤20 |
LSS-I/II:0.67 LSS-C:0.15 LSN-I/II:0.52 LSSF-I:0.67 |
10000 |
| 80 | 22 | 2.2 | 43 | 4.4 | 27 | 2.7 | 87 | 8.9 | 15000 | |||||
| 100 | 24 | 2.4 | 54 | 5.5 | 39 | 4 | 108 | 11 | 15000 | |||||
| 120 | 24 | 2.4 | 54 | 5.5 | 39 | 4 | 86 | 8.8 | 15000 | |||||
| 20 | 50 | 25 | 2.5 | 56 | 5.7 | 34 | 3.5 | 98 | 10 | 6500 | 3500 | ≤20 |
LSS-I/II:0.96 LSS-C:0.28 LSN-I/II:0.73 LSSF-I:0.96 |
10000 |
| 80 | 34 | 3.5 | 74 | 7.5 | 47 | 4.8 | 127 | 13 | 15000 | |||||
| 100 | 40 | 4.1 | 82 | 8.4 | 49 | 5 | 147 | 15 | 15000 | |||||
| 120 | 40 | 4.1 | 87 | 8.9 | 49 | 5 | 147 | 15 | 15000 | |||||
| 160 | 40 | 4.1 | 92 | 9.4 | 49 | 5 | 147 | 15 | 15000 | |||||
| 25 | 50 | 39 | 4 | 98 | 10 | 55 | 5.6 | 186 | 19 | 5600 | 3500 | ≤20 |
LSS-I/II:1.46 LSS-C:0.42 LSN-I/II:1.14 LSSF-I:1.46 |
10000 |
| 80 | 63 | 6.4 | 137 | 14 | 87 | 8.9 | 255 | 26 | 15000 | |||||
| 100 | 67 | 6.8 | 157 | 16 | 108 | 11 | 284 | 29 | 15000 | |||||
| 120 | 67 | 6.8 | 167 | 17 | 108 | 11 | 304 | 31 | 15000 | |||||
| 32 | 50 | 76 | 7.8 | 216 | 22 | 108 | 11 | 382 | 39 | 4800 | 3500 | ≤20 |
LSS-I/II:3.11 LSS-C:0.89 LSN-I/II:2.47 |
10000 |
| 80 | 118 | 12 | 304 | 31 | 167 | 17 | 568 | 58 | 15000 | |||||
| 100 | 137 | 14 | 333 | 34 | 216 | 22 | 647 | 66 | 15000 | |||||
| 120 | 137 | 14 | 353 | 36 | 216 | 22 | 686 | 70 | 15000 | |||||
| 40 | 50 | 137 | 14 | 402 | 41 | 196 | 20 | 686 | 70 | 4000 | 3000 | ≤20 |
LSS-I/II:4.6 LSS-C:1.7 LSN-I/II:3.64 LSSF-I:4.6 |
10000 |
| 80 | 206 | 21 | 519 | 53 | 284 | 29 | 980 | 100 | 15000 | |||||
| 100 | 265 | 27 | 568 | 58 | 372 | 38 | 1080 | 110 | 15000 | |||||
| 120 | 294 | 30 | 617 | 63 | 451 | 46 | 1180 | 120 | 15000 | |||||
-
What is a harmonic drive box?
+A harmonic drive box is a type of gear system that produces high reduction ratios in a compact size. It uses the mechanics of a flexible element deforming to transmit motion and achieve high precision and torque.
-
How does a harmonic gear box work?
+A harmonic gear box works by using a circular spline, flexspline, and a wave generator. The wave generator deforms the flexspline into an elliptical shape, which then engages with the teeth of the circular spline at two points, providing a high reduction ratio through the difference in tooth count between the engaged elements.
-
What are the main components of a strain wave drive?
+The main components are the circular spline (fixed outer ring), the flexspline (flexible inner ring with fewer teeth), and the wave generator (an elliptical disc that fits inside the flexspline).
-
What are the advantages of using harmonic/harmonic drive boxes?
+Strain wave/harmonic gearboxes offer high precision, zero backlashes, high torque capacity, compact size, and lightweight. They are also known for their excellent positional accuracy and repeatability.
-
What applications are harmonic-type drives used in?
+They are used in applications requiring high precision and reliability, such as robotics, aerospace, defense, medical equipment, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
-
How do you select a strain wave drive for a specific application?
+Selection depends on factors like torque requirements, desired reduction ratio, space constraints, load capacity, and environmental conditions. It's essential to consult with manufacturers or experts to choose the appropriate model.
-
What are the different types of Strain Wave Gearboxes?
+Circular Spline Gearboxes
Cup-Type Gearboxes
Flat Gearboxes
-
What is a Circular Spline?
+The Circular Spline in Strain Wave Gearboxes are characterized by their robust design.
NEED A ONE-STOP SOLUTION?
We believe in delivering excellent customer service and we are dedicated to our customers.
If you want to know more about our products, prices, and customized services, please contact us with more details, we will respond as soon as possible.






















 Download
Download








